 SpreadSheet - Formula Calculation
SpreadSheet - Formula CalculationFormulas are the basic building blocks for analyzing and calculating worksheet data. A formula is a string containing numbers, operators, worksheet functions, cell references, and names. A formula can contain as many as 1024 characters.
1. Formula Bar
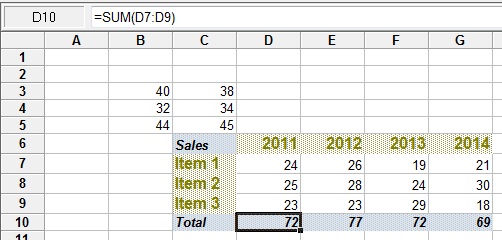
(Figure 1 : Formula Bar)
2. Common Formula Functions
Following are the most commonly used formula functions:
Category |
Common Functions |
Statistical |
AVERAGE, SUM, STDEV, COUNT, COUNTIF, MAX, MIN |
Mathematical |
MOD, CEILING, FLOOR, EXP, FACT, LOG, LOG10, SQRT, TRUNC, ROUND |
Text |
ASC, CONCATENATE, LEFT, LEN, FIND, LOWER, UPPER, MATCH, MID, REPLACE |
Trigonometric |
COS, COSH, ACOS, ACOSH etc. |
Logical |
AND, OR, NOT |
Date & Time |
DATE, DATEVALUE, DAY, DAYS360, MONTH, YEAR, HOUR, MINUTE, TIME, TIMEVALUE, TODAY, NOW |
3. Formula Operators
Arithmetic
Operator |
Meaning |
+ |
Addition |
- |
Subtraction |
/ |
Division |
* |
Multiplication |
% |
Percentage |
^ |
Exponentiation |
Text Comparison
Operator |
Meaning |
& |
Concatenation |
= |
Equal to |
> |
Greater than |
< |
Less than |
>= |
Greater than or equal to |
<= |
Less than or equal to |
<> |
Not equal to |
Reference
Operator |
Meaning |
:, .., . |
Range - produces a reference that includes all the cells between the two references (e.g., A1:A5 includes cells A1 and A5 and all cells in between). |
, |
Union - produces one reference that includes the two references (e.g., A1:A10,C1:C10). |
4. Formula Operator Precedence
The following table lists the order of precedence for formula operators.
Operator |
Description |
( ) |
Parentheses |
:, .., . |
Range |
, |
Union |
- |
Negation (single operand) |
% |
Percentage |
^ |
Exponentiation |
* and / |
Multiplication and Division |
+ and - |
Addition and Subtraction |
& |
Text concatenation |
= < > <= >= <> |
Comparison |
Operators of like precedence are evaluated left to right. Parentheses should be used when it is necessary to change the order of evaluation. The following example illustrates how the result of a formula can be altered by adding parentheses to change the order of precedence.
Formula |
Result |
1+2*37 75 |
7551 |
(1+2)*37 |
111 |
As illustrated in the previous table, the multiplication operator (*) has higher precedence than the addition operator (+). It is evaluated first unless parentheses are used to force the addition to take place first.